Gout: A Comprehensive Guide To Symptoms, Treatment, And Prevention is a thorough resource that can educate readers about this prevalent condition.
Editor's Notes: Gout Gout: A Comprehensive Guide To Symptoms, Treatment, And Prevention was published today. Gout is a type of inflammatory arthritis that can cause severe pain and swelling in the joints. This guide provides comprehensive information on the symptoms, treatment, and prevention of gout, including updated research and treatment options.
After doing some analysis and digging information, we made Gout Gout: A Comprehensive Guide To Symptoms, Treatment, And Prevention, we put together this Gout Gout: A Comprehensive Guide To Symptoms, Treatment, And Prevention guide to help target audience make the right decision.
Key Differences or Key takeaways:
- Symptoms: Gout can cause sudden, severe pain, swelling, redness, and warmth in the joints. The most commonly affected joint is the big toe.
- Treatment: Gout is treated with medications to reduce pain and inflammation, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), colchicine, and corticosteroids.
- Prevention: Gout can be prevented by reducing the intake of purine-rich foods, such as red meat, organ meats, and seafood.
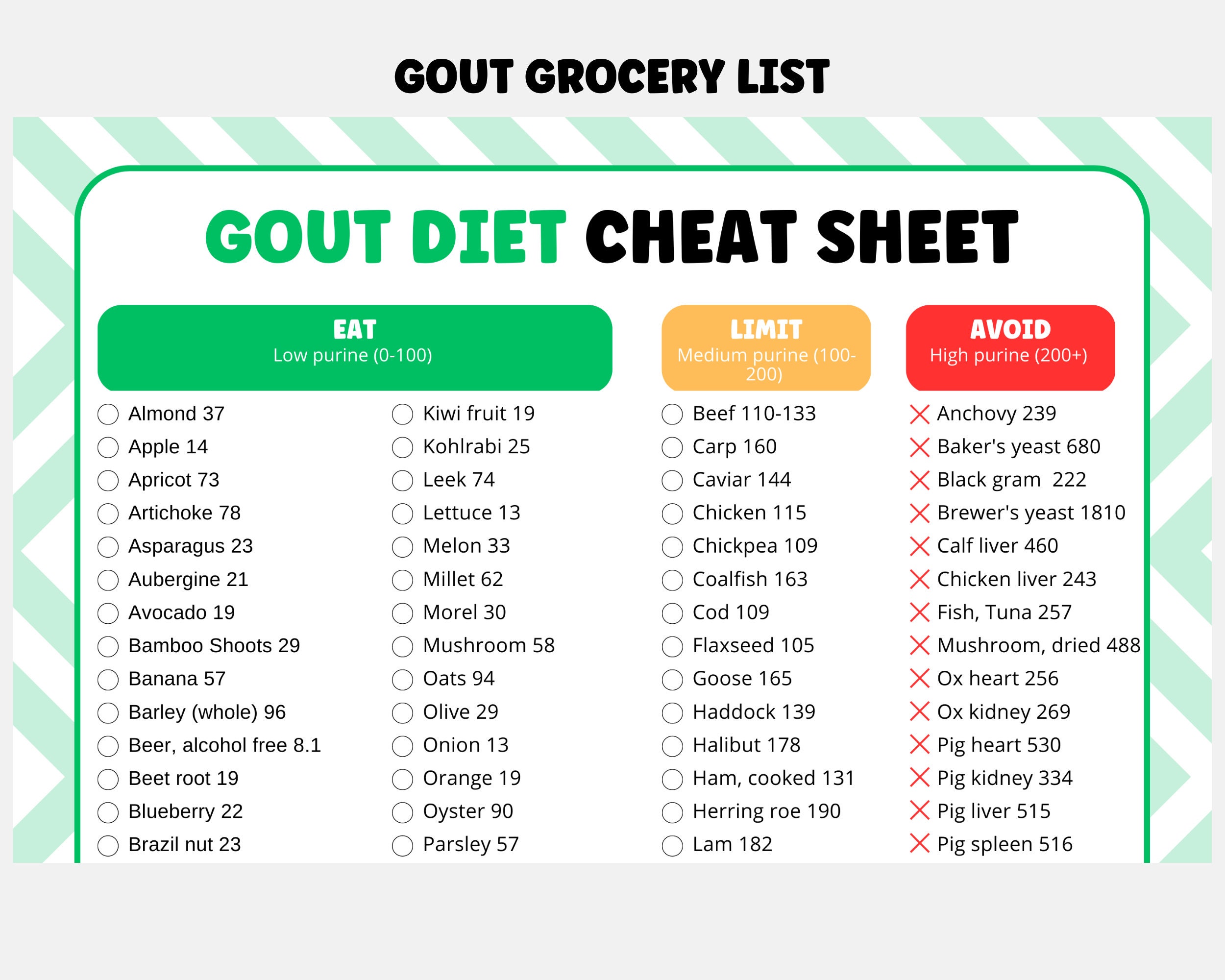
Gout Diet Sheet Nhs Uk - Source garagefixsociableka.z21.web.core.windows.net
Transition to main article topics:
FAQ
This FAQ section provides concise answers to commonly asked questions regarding gout, offering valuable insights to further your understanding of this condition.
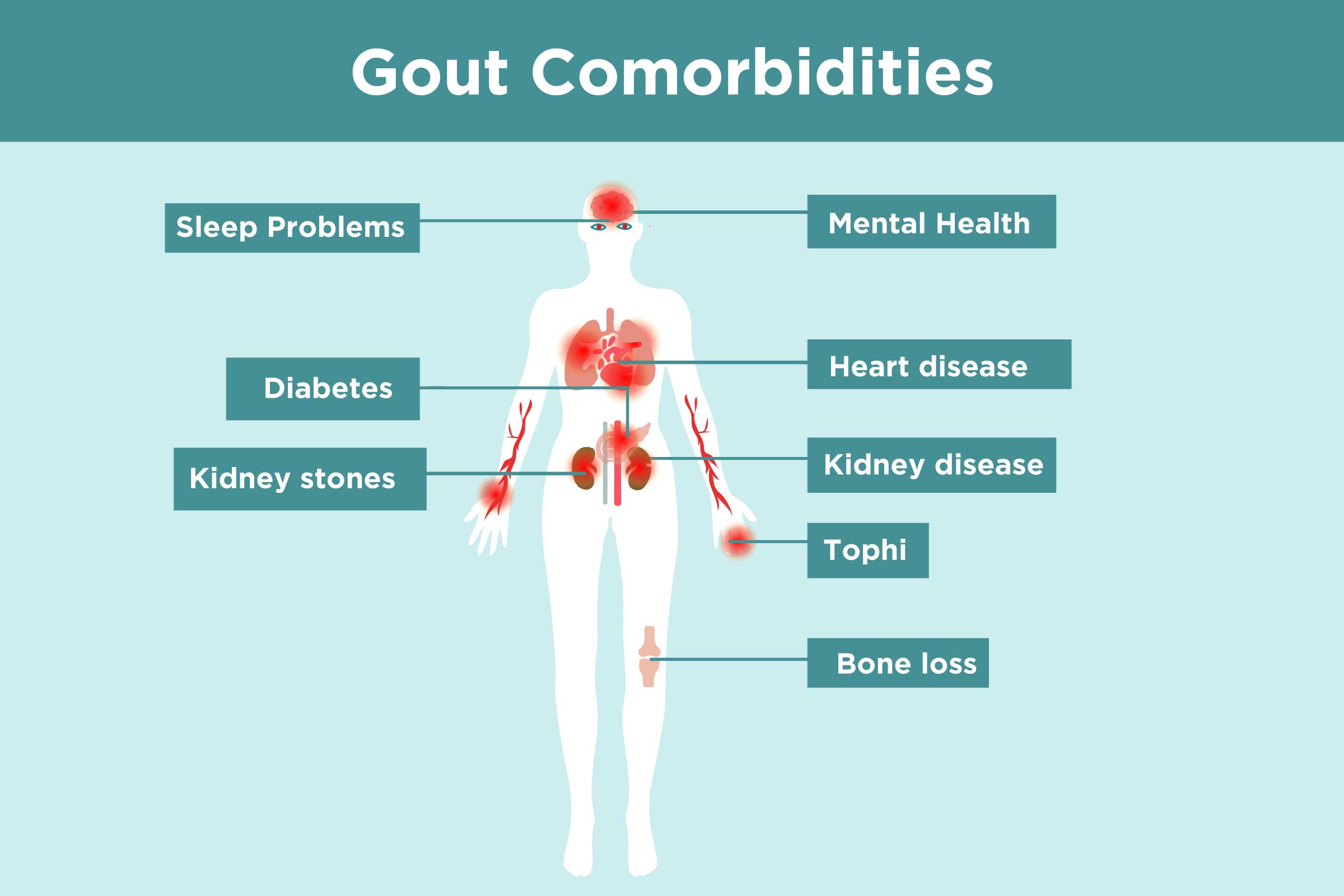
Gout Complications and Comorbidities: What Gout Patients Need to Know - Source creakyjoints.org
Question 1: What are the most common symptoms of gout?
Gout typically manifests as sudden, severe pain, swelling, and redness in one or more joints, often the big toe.
Question 2: What causes gout?
Gout arises from the accumulation of uric acid crystals within joints, which occurs when uric acid levels in the blood become excessively high.
Question 3: How is gout diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a physical examination, a review of symptoms, and blood tests to measure uric acid levels and rule out other conditions.
Question 4: What are the treatment options for gout?
Treatment aims to reduce pain and inflammation, prevent future attacks, and lower uric acid levels. Medications, lifestyle modifications, and in severe cases, surgery may be employed.
Question 5: How can I prevent gout attacks?
Maintaining a healthy weight, adopting a balanced diet low in purines, and limiting alcohol intake can help reduce the risk of gout.
Question 6: Is gout curable?
While there is no definitive cure for gout, proper management and adherence to treatment plans can effectively control symptoms and prevent complications.
Summary:
Gout, characterized by sudden and painful joint inflammation, is caused by excess uric acid in the blood. Diagnosis involves physical examination, symptom analysis, and blood tests. Treatment focuses on alleviating symptoms, preventing attacks, and lowering uric acid levels.
Next Article Section: Prevention and Dietary Management of Gout
Tips
To prevent gout attacks and manage symptoms, consider implementing these effective tips:
Tip 1: Maintain a Healthy Diet
Reduce purine intake by limiting red meat, organ meats, and seafood. Include fruits, vegetables, and low-fat dairy products in your diet.
Tip 2: Manage Weight
Obesity increases uric acid production. Reach a healthy weight and maintain it through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
Tip 3: Stay Hydrated
Drink plenty of fluids, especially water, to dilute uric acid and promote its excretion.
Tip 4: Limit Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol, particularly beer, can increase uric acid levels. Limit or avoid alcohol intake to prevent gout attacks.
Tip 5: Medications
Consult your healthcare provider about medications to lower uric acid levels, such as allopurinol, febuxostat, or colchicine.
Tip 6: Avoid Triggers
Identify and avoid potential triggers for gout attacks, such as certain foods, stress, or strenuous exercise.
Tip 7: Quit Smoking
Smoking can increase uric acid levels and worsen gout symptoms. Quitting smoking can significantly improve overall health and reduce gout risk.
For more comprehensive information on gout, refer to
Gout Gout: A Comprehensive Guide To Symptoms, Treatment, And Prevention
.
Gout Gout: A Comprehensive Guide To Symptoms, Treatment, And Prevention
Gout, a form of inflammatory arthritis, is a complex condition that requires a multifaceted approach to management. This guide will explore six key aspects crucial for understanding and addressing gout, providing a comprehensive overview of symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures.
- Symptoms: Intense joint pain, swelling, redness, and heat.
- Causes: High levels of uric acid in the blood, leading to crystal formation in joints.
- Diagnosis: Physical examination, blood tests, and imaging techniques.
- Treatment: Medications to reduce pain and inflammation, and to lower uric acid levels.
- Prevention: Dietary modifications, maintaining a healthy weight, and managing underlying medical conditions.
- Lifestyle: Avoiding alcohol, sugary drinks, and foods high in purines can help prevent gout attacks.
Understanding these aspects empowers individuals to proactively manage their gout and improve their overall well-being. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment can effectively alleviate symptoms, reduce the risk of complications, and improve quality of life. Dietary changes, lifestyle modifications, and adherence to medication regimens play a crucial role in preventing future gout attacks and maintaining joint health.
Gout Gout: A Comprehensive Guide To Symptoms, Treatment, And Prevention
Gout is a common form of inflammatory arthritis that is caused by the deposition of urate crystals in the joints. It is characterized by sudden, severe pain, swelling, and redness in the affected joint. Gout can affect any joint in the body, but it most commonly affects the big toe.

Gout Arthritis: 4 Phase Development Of Gout Arthritis – Singapore - Source www.singaporesportsclinic.com
Gout is caused by a build-up of uric acid in the blood. Uric acid is a waste product that is produced when the body breaks down purines. Purines are found in many foods, including red meat, organ meats, and seafood.
The connection between "Gout Gout: A Comprehensive Guide To Symptoms, Treatment, And Prevention", symptoms, treatment, and prevention is important for several reasons. First, it provides a comprehensive overview of the condition, including its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. This information can help patients better understand their condition and make informed decisions about their care.
Second, the guide can help patients prevent gout attacks. By following the recommendations in the guide, patients can reduce their risk of developing gout or having a gout attack.
Third, the guide can help patients manage their gout attacks. By following the recommendations in the guide, patients can reduce the severity and duration of their gout attacks.
Finally, the guide can help patients improve their quality of life. Gout can be a debilitating condition, but by following the recommendations in the guide, patients can improve their quality of life and live a more active and fulfilling life.
The following table provides a summary of the key points covered in "Gout Gout: A Comprehensive Guide To Symptoms, Treatment, And Prevention":
| Topic | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Causes of Gout | Gout is caused by a build-up of uric acid in the blood. Uric acid is a waste product that is produced when the body breaks down purines. Purines are found in many foods, including red meat, organ meats, and seafood. |
| Symptoms of Gout | Gout is characterized by sudden, severe pain, swelling, and redness in the affected joint. Gout can affect any joint in the body, but it most commonly affects the big toe. |
| Treatment of Gout | The treatment of gout involves reducing uric acid levels in the blood. This can be done through medication, diet, and lifestyle changes. |
| Prevention of Gout | Gout can be prevented by following a healthy diet, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding alcohol. |
Conclusion
Gout is a common and treatable condition. By following the recommendations in "Gout Gout: A Comprehensive Guide To Symptoms, Treatment, And Prevention", patients can reduce their risk of developing gout or having a gout attack, manage their gout attacks, and improve their quality of life.
If you are experiencing symptoms of gout, it is important to see a doctor right away. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent serious complications.